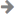YOLOv5 实例分割-Labelme标注与json文件转txt
labelme启动方法请参考博客:Labelme安装与运行
打开labelme之后,使用Create Polygons沿着我们需要检测的目标轮廓进行进行多边形标注,如下:

标注完之后,使用下面代码将labelme标注的*.json文件转换成yolov5_v7.0sege数据集文件*.txt
import json
import os
import glob
import os.path as osp
def labelme2yolov2Seg(jsonfilePath="", resultDirPath="", classList=["YiBiao", "ZhiZhen"]):
"""
此函数用来将labelme软件标注好的数据集转换为yolov5_7.0sege中使用的数据集
:param jsonfilePath: labelme标注好的*.json文件所在文件夹
:param resultDirPath: 转换好后的*.txt保存文件夹
:param classList: 数据集中的类别标签
:return:
"""
# 0.创建保存转换结果的文件夹
if(not os.path.exists(resultDirPath)):
os.mkdir(resultDirPath)
# 1.获取目录下所有的labelme标注好的Json文件,存入列表中
jsonfileList = glob.glob(osp.join(jsonfilePath, "*.json"))
print(jsonfileList) # 打印文件夹下的文件名称
# 2.遍历json文件,进行转换
for jsonfile in jsonfileList:
# 3. 打开json文件
with open(jsonfile, "r") as f:
file_in = json.load(f)
# 4. 读取文件中记录的所有标注目标
shapes = file_in["shapes"]
# 5. 使用图像名称创建一个txt文件,用来保存数据
with open(resultDirPath + "\\" + jsonfile.split("\\")[-1].replace(".json", ".txt"), "w") as file_handle:
# 6. 遍历shapes中的每个目标的轮廓
for shape in shapes:
# 7.根据json中目标的类别标签,从classList中寻找类别的ID,然后写入txt文件中
file_handle.writelines(str(classList.index(shape["label"])) + " ")
# 8. 遍历shape轮廓中的每个点,每个点要进行图像尺寸的缩放,即x/width, y/height
for point in shape["points"]:
x = point[0]/file_in["imageWidth"] # mask轮廓中一点的X坐标
y = point[1]/file_in["imageHeight"] # mask轮廓中一点的Y坐标
file_handle.writelines(str(x) + " " + str(y) + " ") # 写入mask轮廓点
# 9.每个物体一行数据,一个物体遍历完成后需要换行
file_handle.writelines("\n")
# 10.所有物体都遍历完,需要关闭文件
file_handle.close()
# 10.所有物体都遍历完,需要关闭文件
f.close()
if __name__ == "__main__":
jsonfilePath = "E:\\yolo\\yolov5-master\\datasets\\labelme\\json" # 要转换的json文件所在目录
resultDirPath = "E:\\yolo\\yolov5-master\\datasets\\labelme\\txt" # 要生成的txt文件夹
labelme2yolov2Seg(jsonfilePath=jsonfilePath, resultDirPath=resultDirPath, classList=["YiBiao", "ZhiZhen"])
然后将我们的jpg图片和转换后的txt文件按“coco128-seg”数据集格式,扔到datasets目录下,最后进行识别测试,测试结果如下:
代码优化
博主对上面代码重新优化了一下,如下:
'''
将json文件转为yolo所需要的txt文件。将未转换的标注放入labels文件夹中,图片放入images文件夹中
json中[x1,y1,x2,y2],(x1,y1)表示目标左上角坐标,(x2,y2)表示目标右下角坐标,图片左上角坐标为(0,0)
yolo的txt中[class,x_center,y_center,width,height](需要根据图片宽高进行归一化处理)
yolo(类别 中心点的x 中心点的y 宽度w 高度h)
'''
import json
import os
from PIL import Image
def convert(img_size, box): # 坐标转换
dw = 1. / (img_size[0])
dh = 1. / (img_size[1])
x = (box[0] + box[2]) / 2.0
y = (box[1] + box[3]) / 2.0
# 左上到右下,否则负数
w = box[2] - box[0]
h = box[3] - box[1]
x = x * dw
w = w * dw
y = y * dh
h = h * dh
return x, y, w, h
def decode_json(json_floder_path, json_name):
# txt输出路径
txtpath = 'yolov5-master/datasets/coco/labels/train2017/'
txt_name = txtpath + json_name[0:-5] + '.txt' # 生成txt文件存放的路径
print(txt_name)
txt_file = open(txt_name, 'w')
json_path = os.path.join(json_floder_path, json_name)
data = json.load(open(json_path, 'r', encoding='utf-8'))
# 图片路径
imgpath = 'yolov5-master/datasets/labelme/'
image_path = imgpath + json_name[0:-5] + '.jpg' # 图片存放路径
# 使用pillow读取图片,获取图片的宽和高
img_pillow = Image.open(image_path)
img_w = img_pillow.width # 图片宽度
img_h = img_pillow.height # 图片高度
print(image_path, img_w, img_h)
# 所有样本名称列表
labels = ['person', 'bicycle', 'car']
for i in data['shapes']:
for index, label in enumerate(labels):
if i['label'] == label:
x1, y1 = i['points'][0]
x2, y2 = i['points'][1]
bb = (x1, y1, x2, y2)
bbox = convert((img_w, img_h), bb)
txt_file.write(str(index) + " " + " ".join([str(a) for a in bbox]) + '\n')
break
if __name__ == "__main__":
json_floder_path = 'yolov5-master/datasets/labelme' # json文件的路径
json_names = os.listdir(json_floder_path)
for json_name in json_names:
if json_name.split(".")[-1] == "json":
decode_json(json_floder_path, json_name)